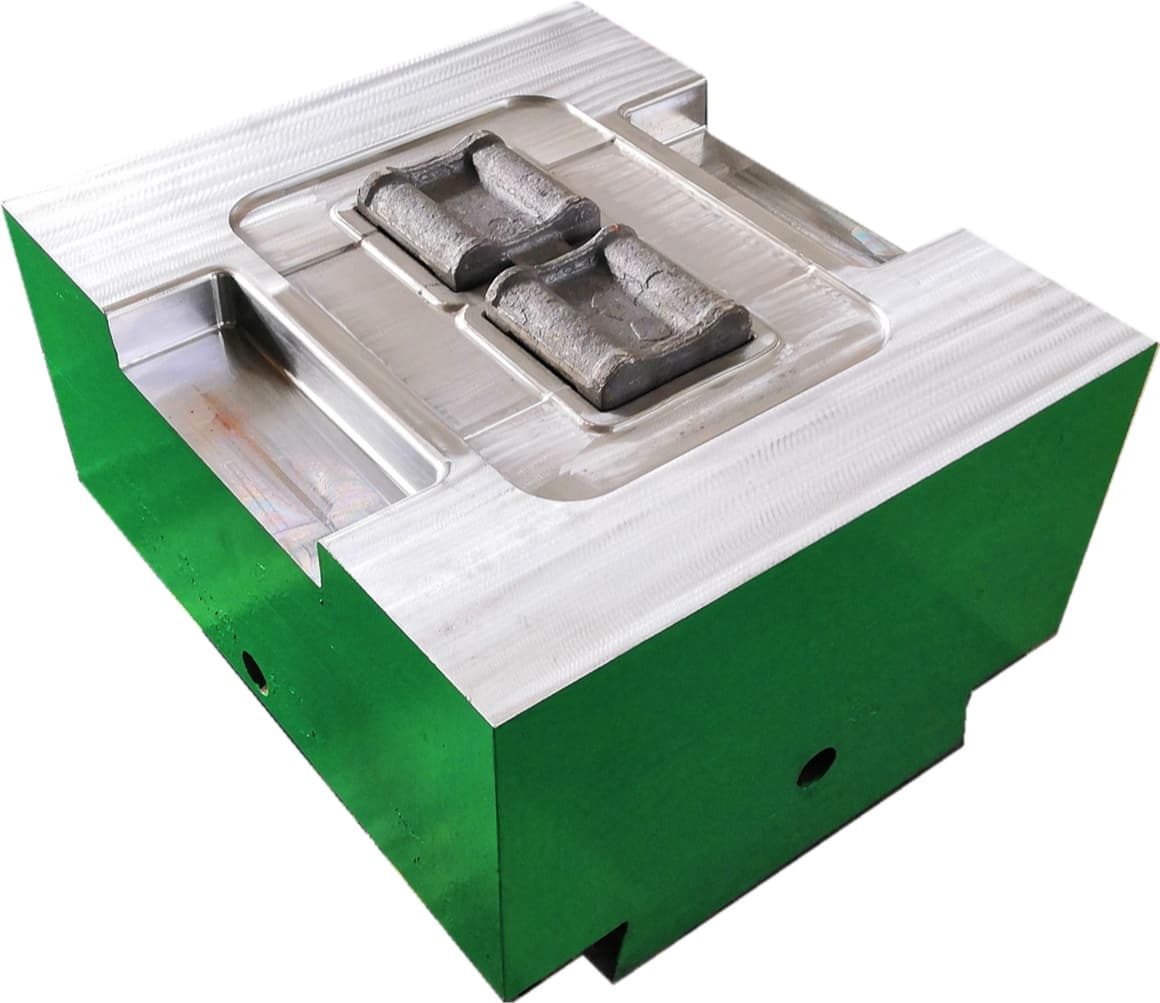
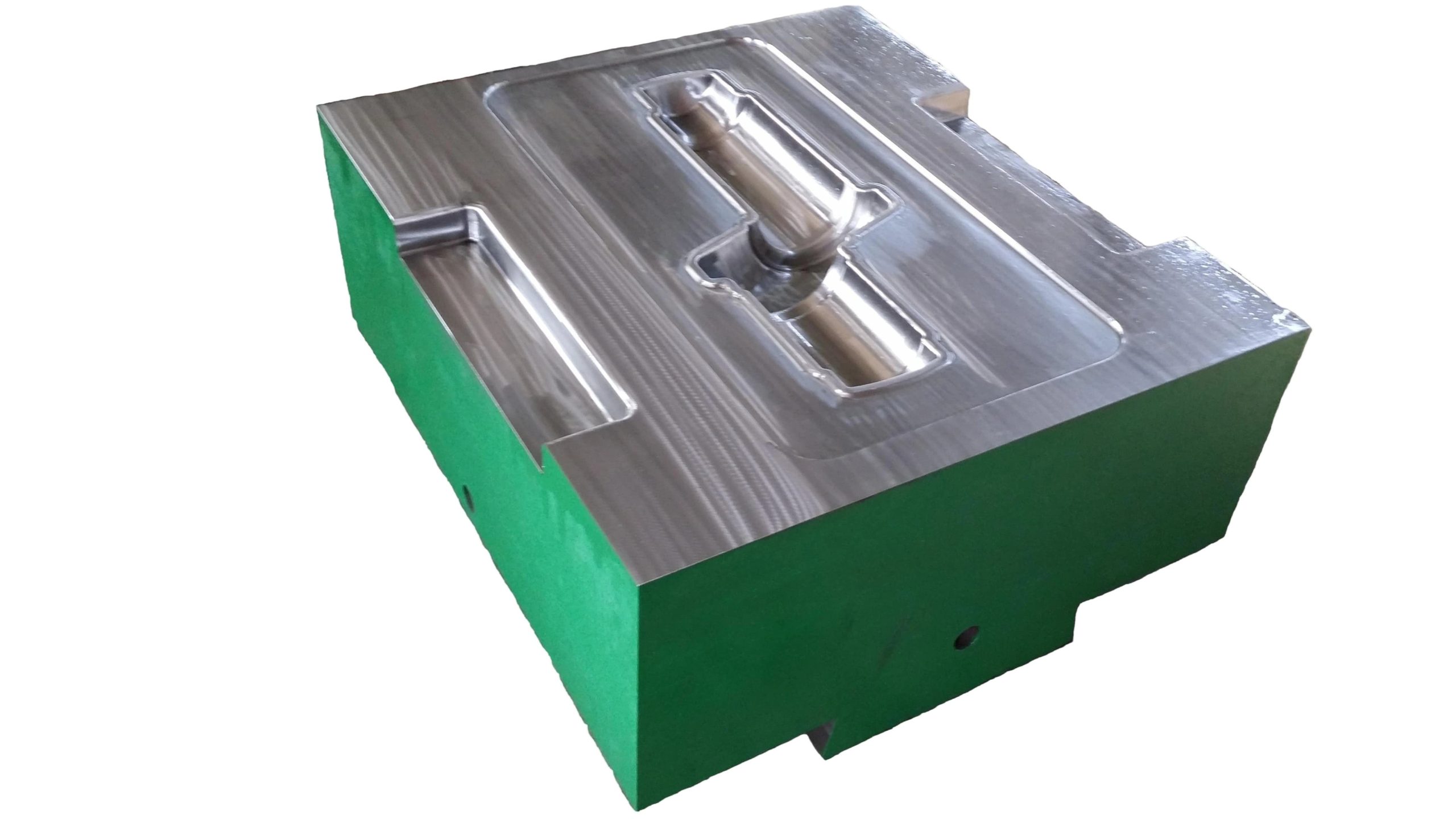
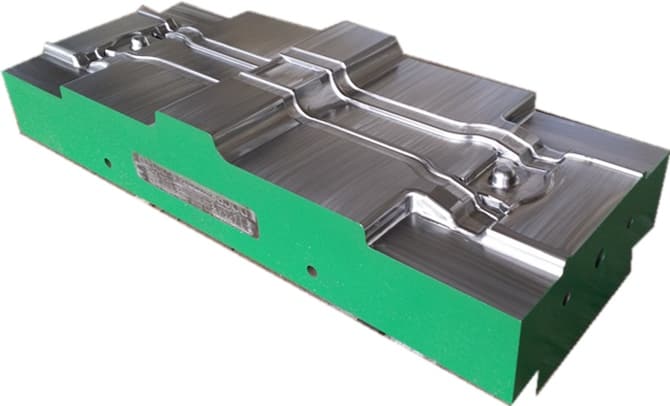
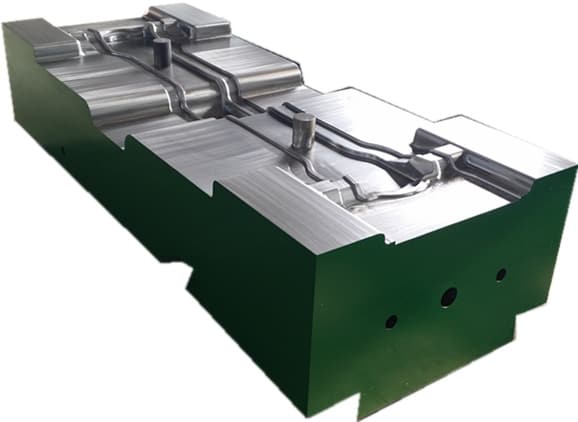
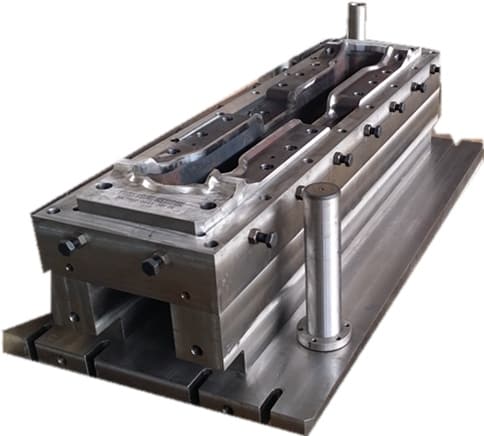
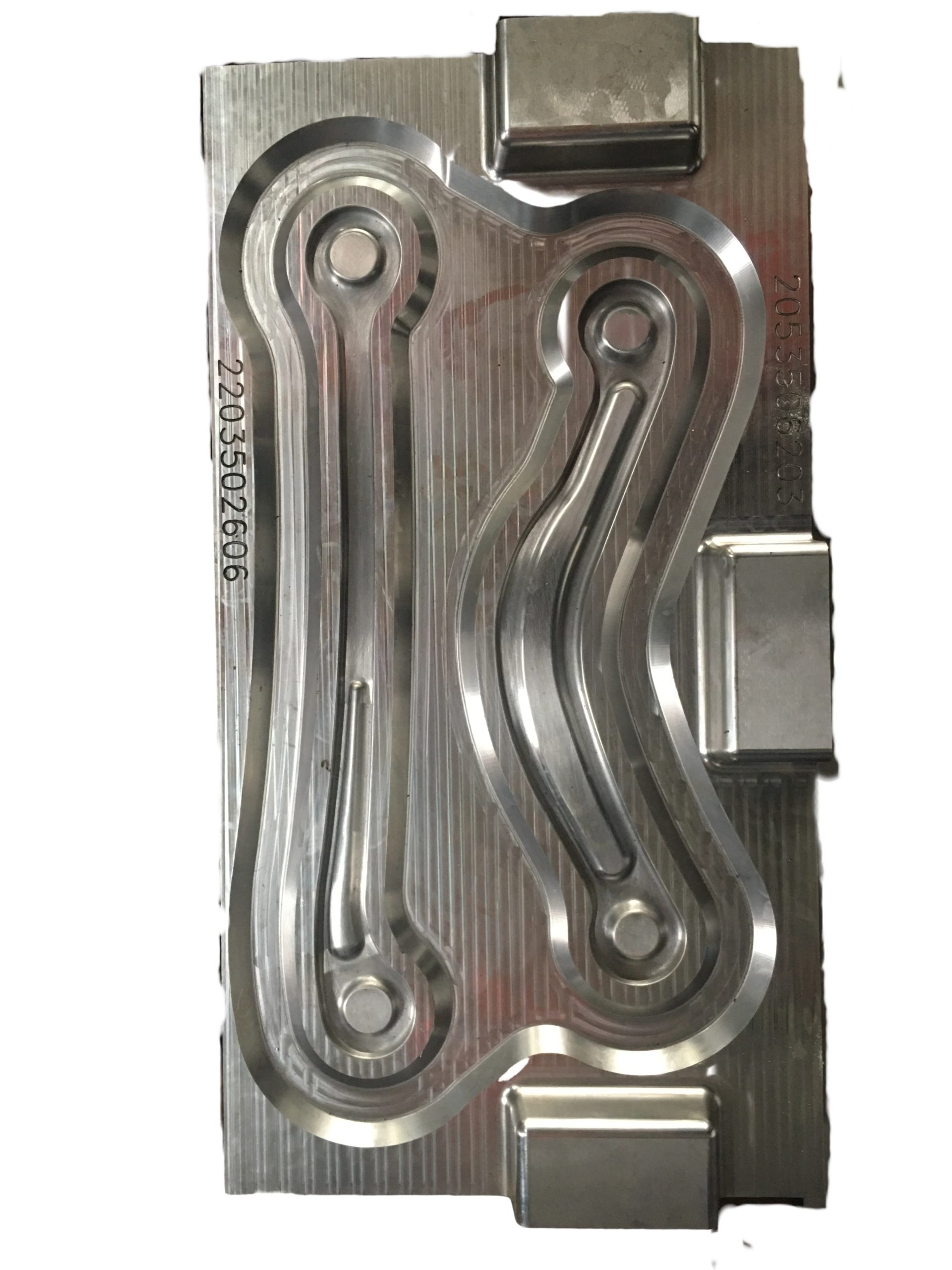
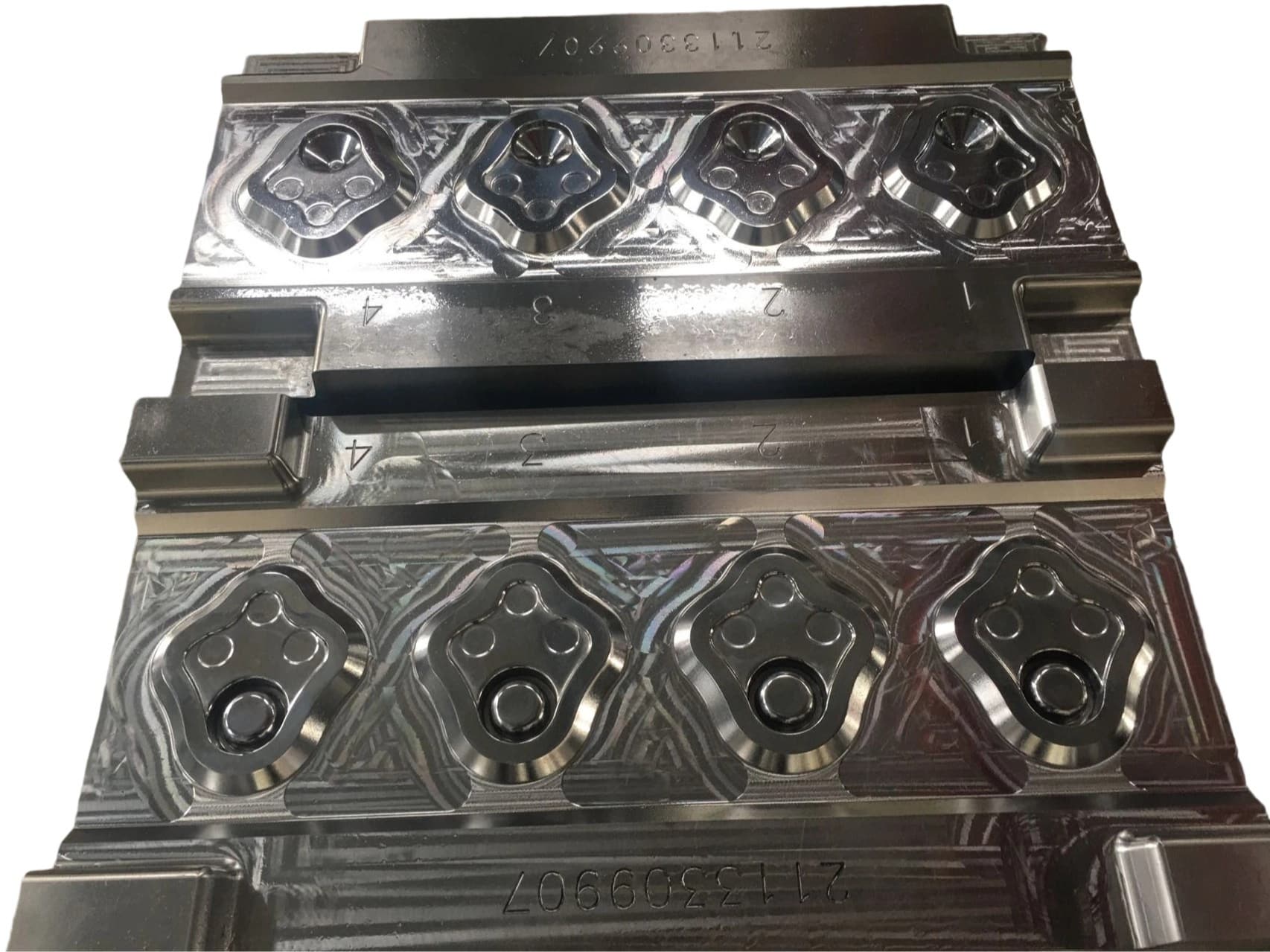
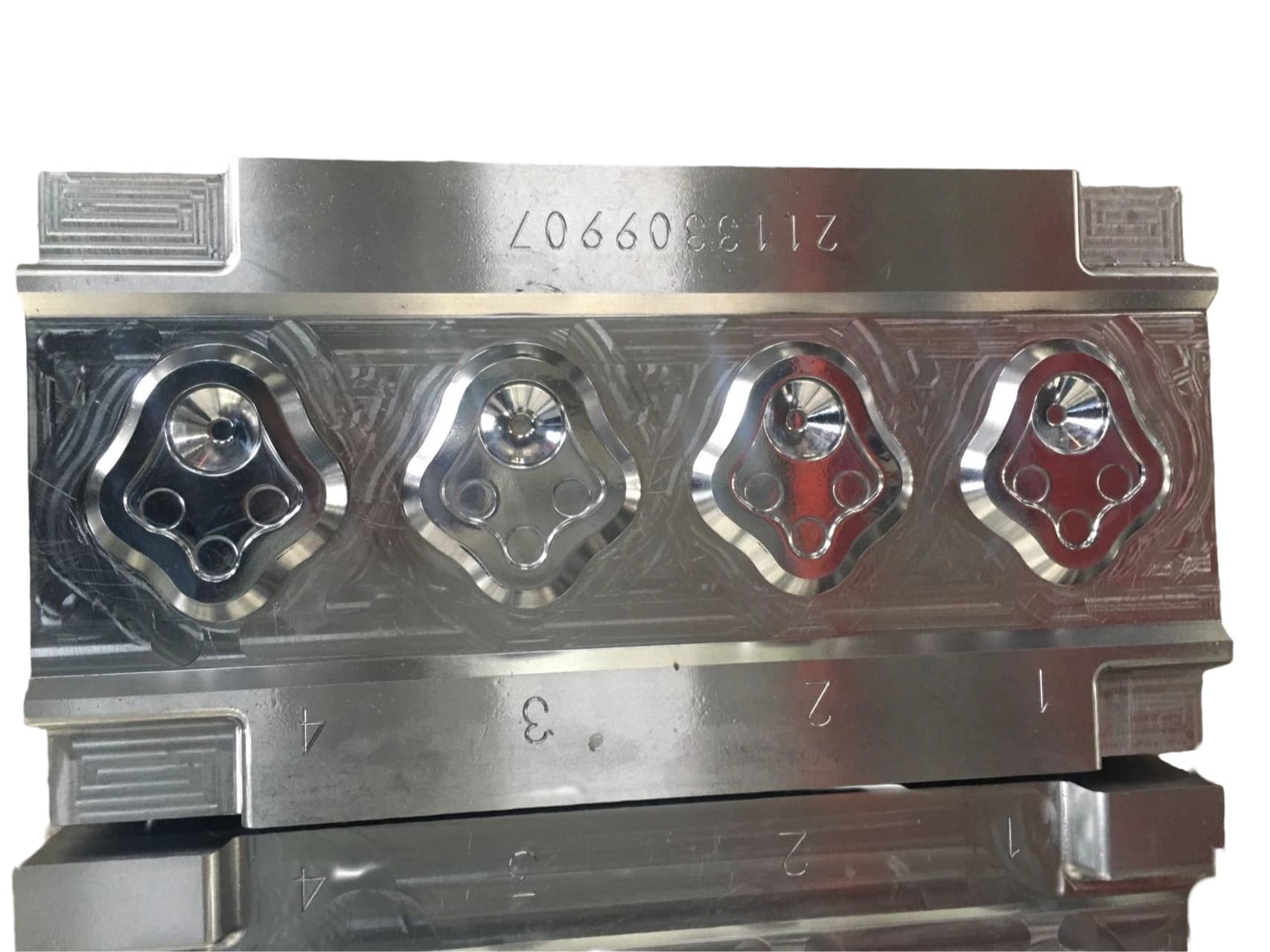
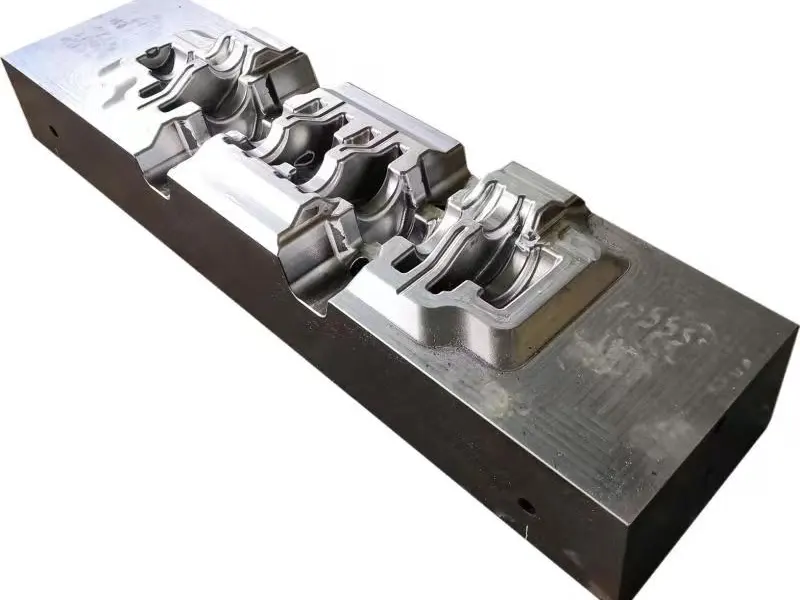
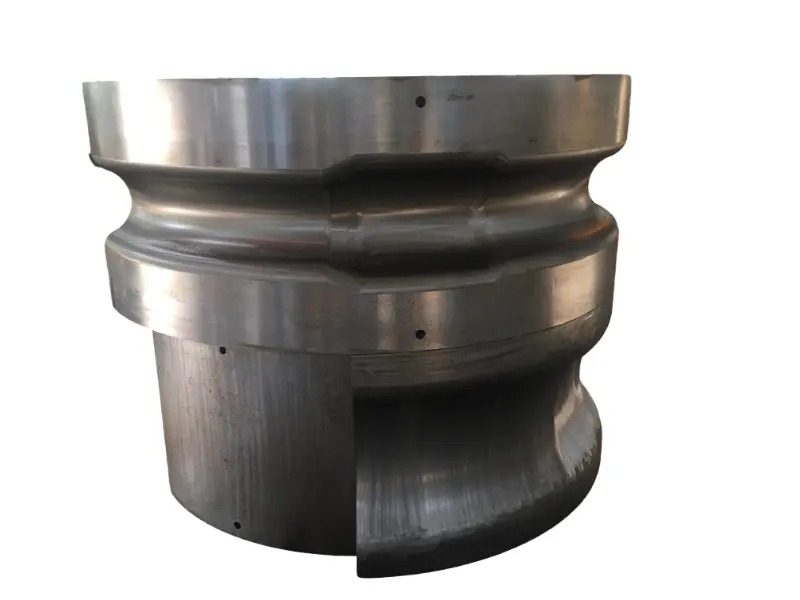
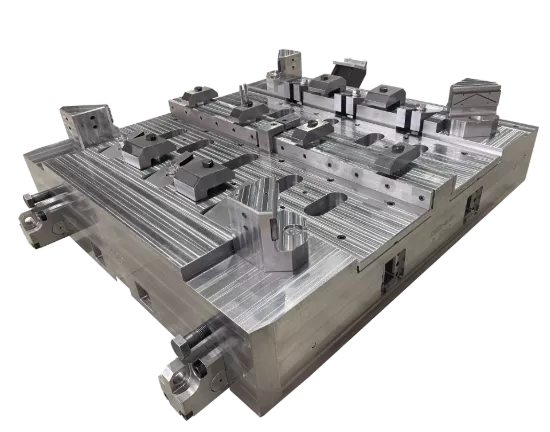
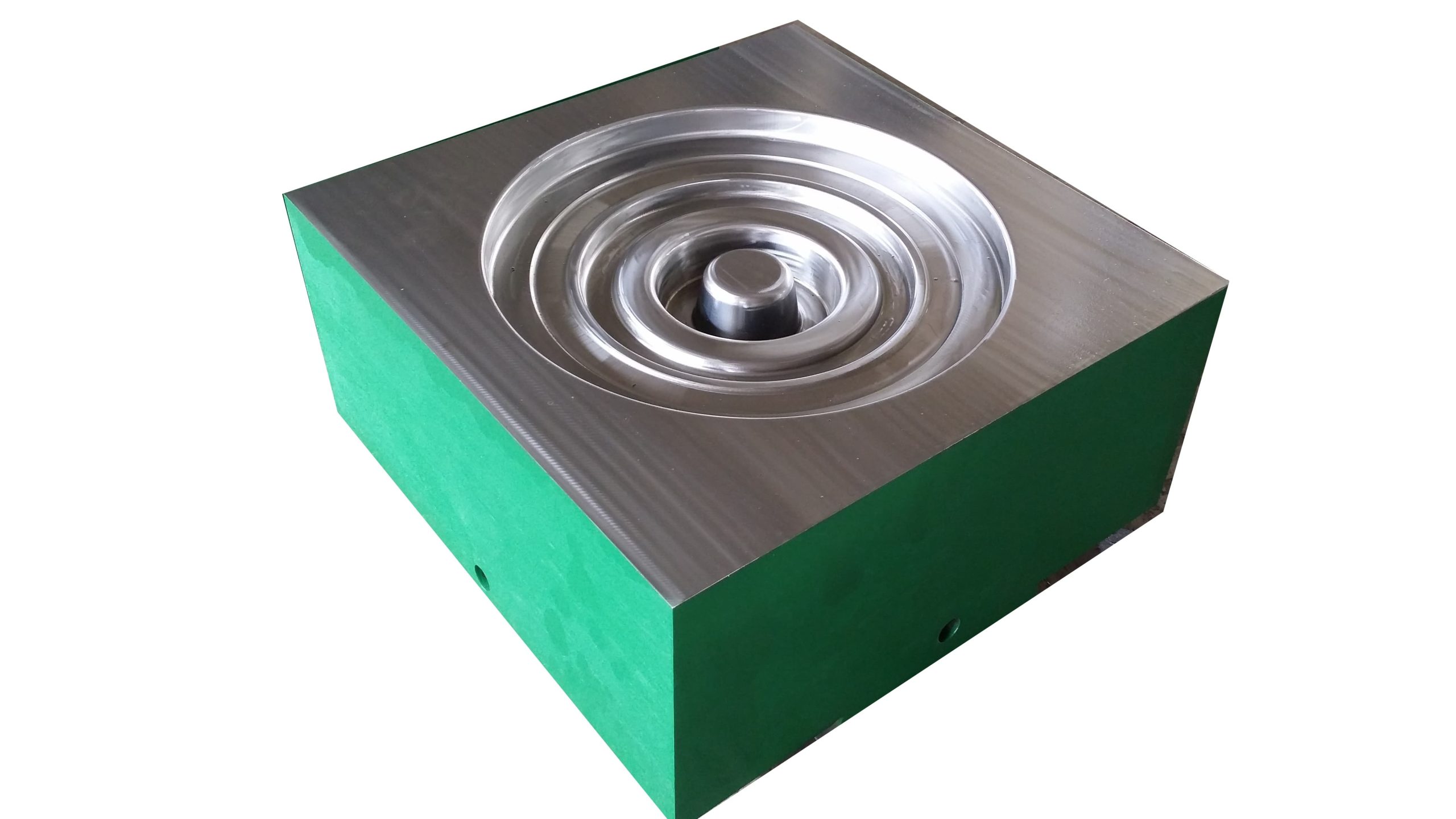
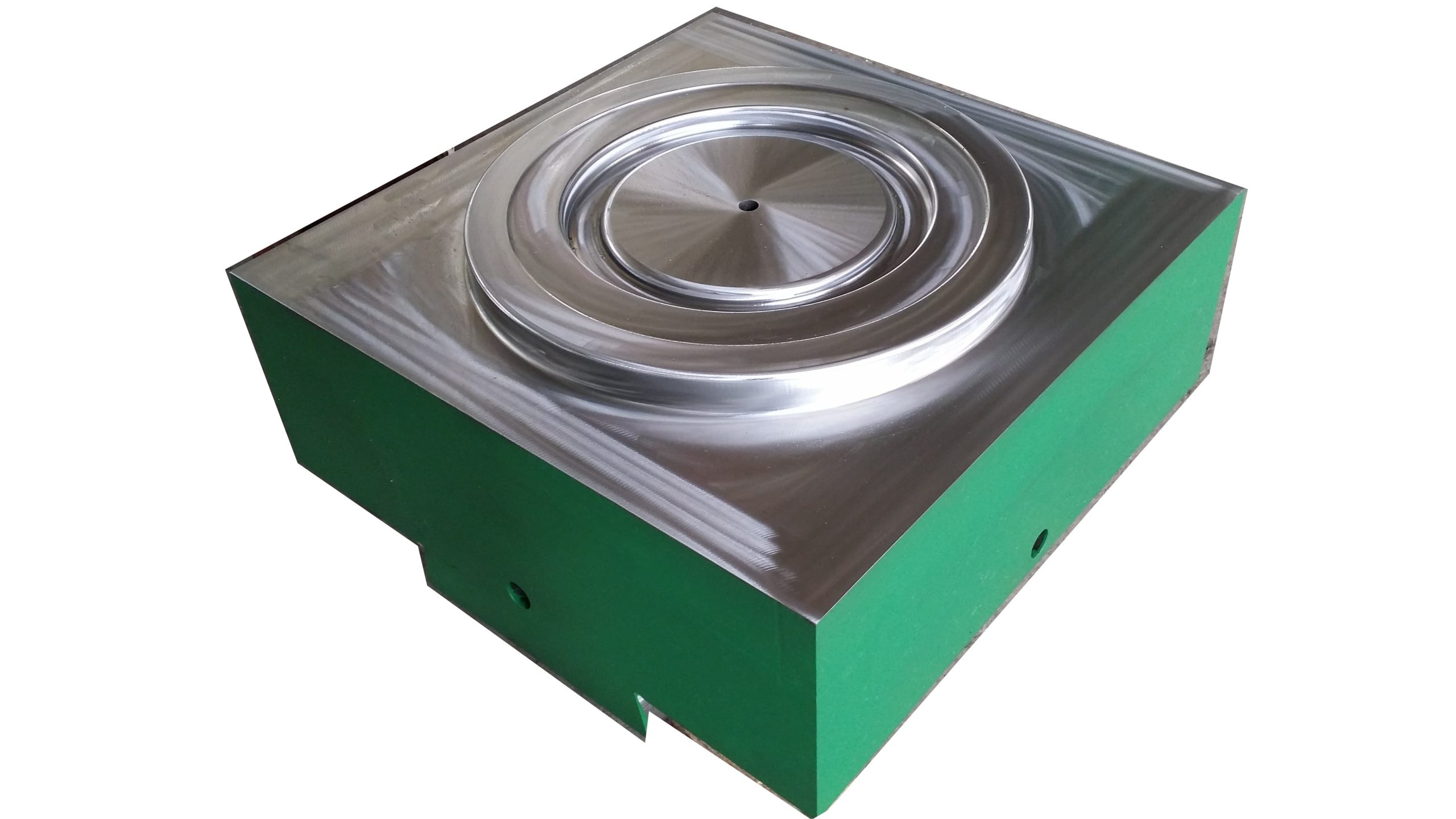
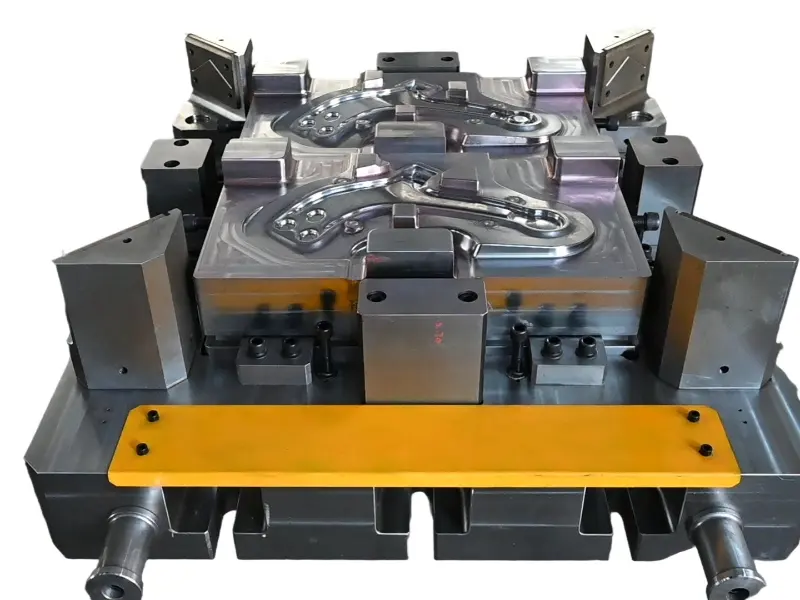
Closed forging die, also known as no flash forging die, is a professional fixture that achieves precise forming of metal billets through a closed cavity. With its core advantages of "no flash, high precision, and high material utilization", it has become a key equipment for precision forging production in the high-end mechanical manufacturing field. Its structural design is centered around "fully enclosed cavity and controllable force", mainly composed of upper mold, lower mold, guide mechanism, ejector mechanism, and locking mechanism.
In terms of process adaptability, closed forging molds can be compatible with various advanced forging processes, such as warm forging, hot forging, and cold forging (for low carbon steel/non-ferrous metals), and can design split type cavities or combination molds according to the characteristics of forgings (such as complex inner cavities and thin-walled structures) to meet the forming needs of precision forgings with different shapes (such as gears, bearing rings, connecting rods, hydraulic valve blocks).
Closed forging die
steel:1.2714 / 1.2365 / H13 / 5CrNiMo / 5CrNiMoV / 5CrMnMo / 40CrNiMoA, etc.
Product Description:
Product Usage
Closed forging dies are widely used in fields with strict requirements for forging accuracy, mechanical properties, and cost control due to their characteristics of “high precision, low loss, and high efficiency”. Their main applications are concentrated in the following scenarios:
Manufacturing of precision parts for general machinery and medical devices
In the field of general machinery, closed forging molds are used to produce parts such as motor rotors, water pump impellers, compressor connecting rods, etc. By forging without flying edges, material waste is reduced, while improving the mechanical properties of the parts and reducing subsequent processing costs; In the field of medical devices, titanium alloy forgings are used to produce artificial joints. The mold cavity is strictly designed according to the human skeletal structure, and the forged forgings have high dimensional accuracy and smooth surfaces
Manufacturing of automotive core precision forgings
This is the main application area of closed forging molds, mainly used for producing precision forgings for automotive transmission systems, chassis systems, and engine systems. The control arm and steering knuckle of the car chassis can be continuously distributed with metal fibers inside the forging through closed forging, significantly improving the impact strength and fatigue life, and ensuring the safety of car driving; The motor shaft and reducer housing of new energy vehicles also rely on closed molds to achieve high-precision molding, reducing subsequent machining and lowering production costs.
Manufacturing of high-end hydraulic components for construction machinery
The core components of hydraulic systems in construction machinery such as excavators, loaders, and cranes, including hydraulic pump cylinders, valve cores, and plungers. The mold can be designed with a dedicated cavity based on the complex internal cavity structure of hydraulic components (such as multiple oil channels and stepped holes), allowing the metal blank to completely fill the cavity under high pressure, forming a dense metal structure, avoiding internal looseness, porosity and other defects caused by casting or open forging, ensuring that hydraulic components do not leak under high pressure conditions, and improving the stability and service life of the hydraulic system.
Manufacturing of precision forgings for rail transit and aerospace
In the field of rail transit, closed forging molds are used to produce axle boxes and wheelset components (such as bearing inner and outer rings) for high-speed trains and subways; In the aerospace field, molds can be used to produce precision forgings such as blade tenons and fuselage connection joints for aircraft engines. High temperature alloy closed forging is used to refine the internal grain size and uniform mechanical properties of the forgings, meeting the needs of aerospace equipment in extreme environments (high temperature, high pressure, high corrosion).