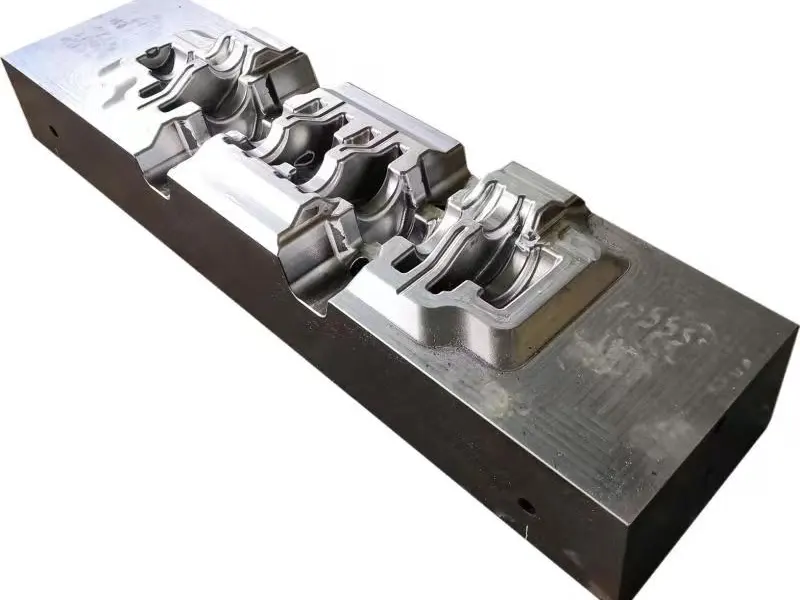
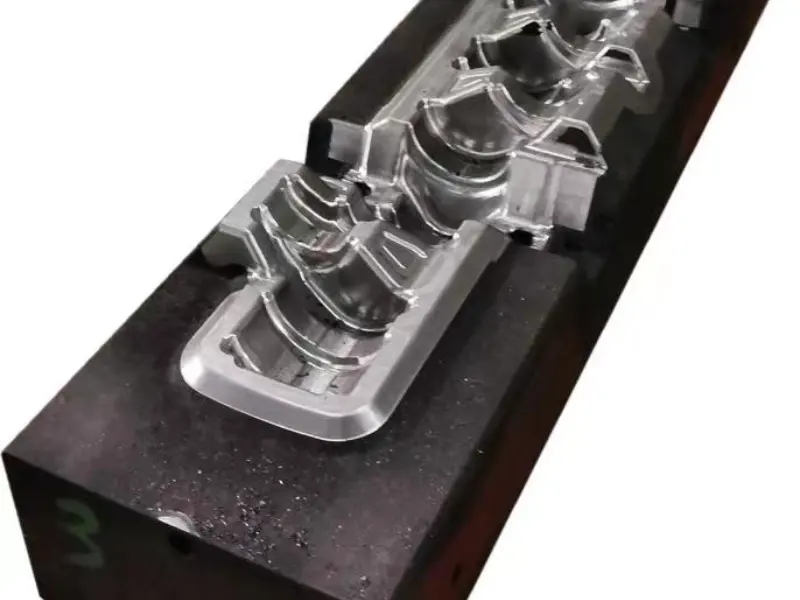
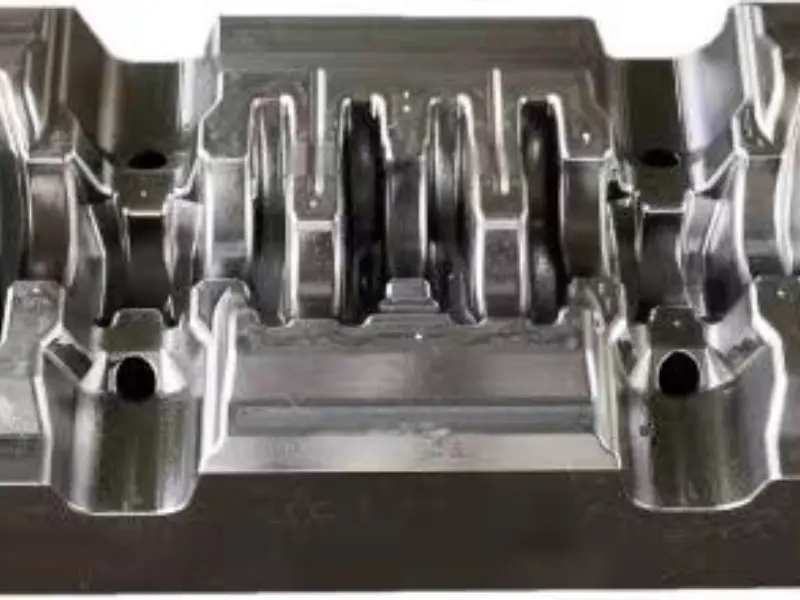
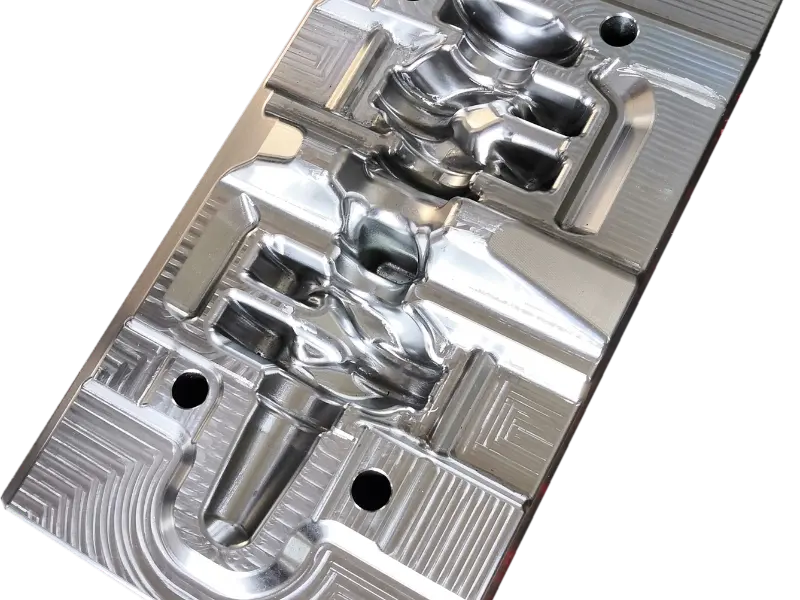
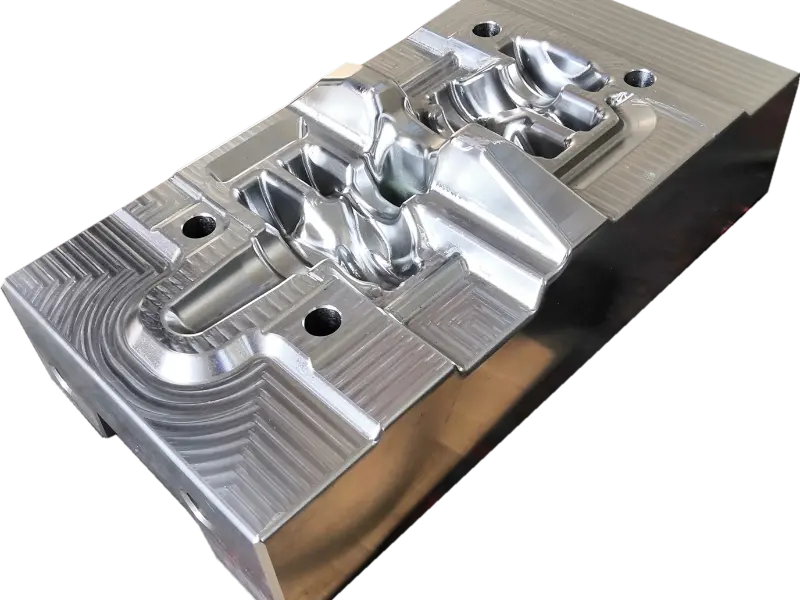
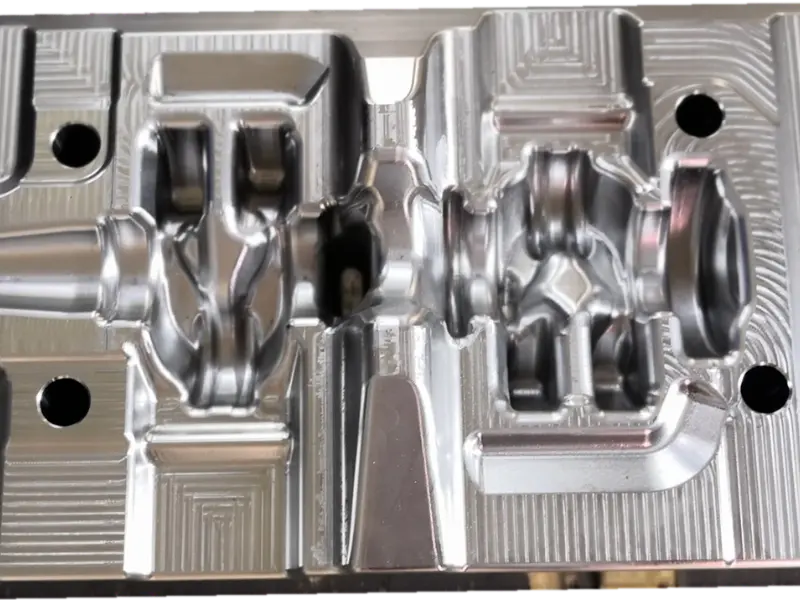
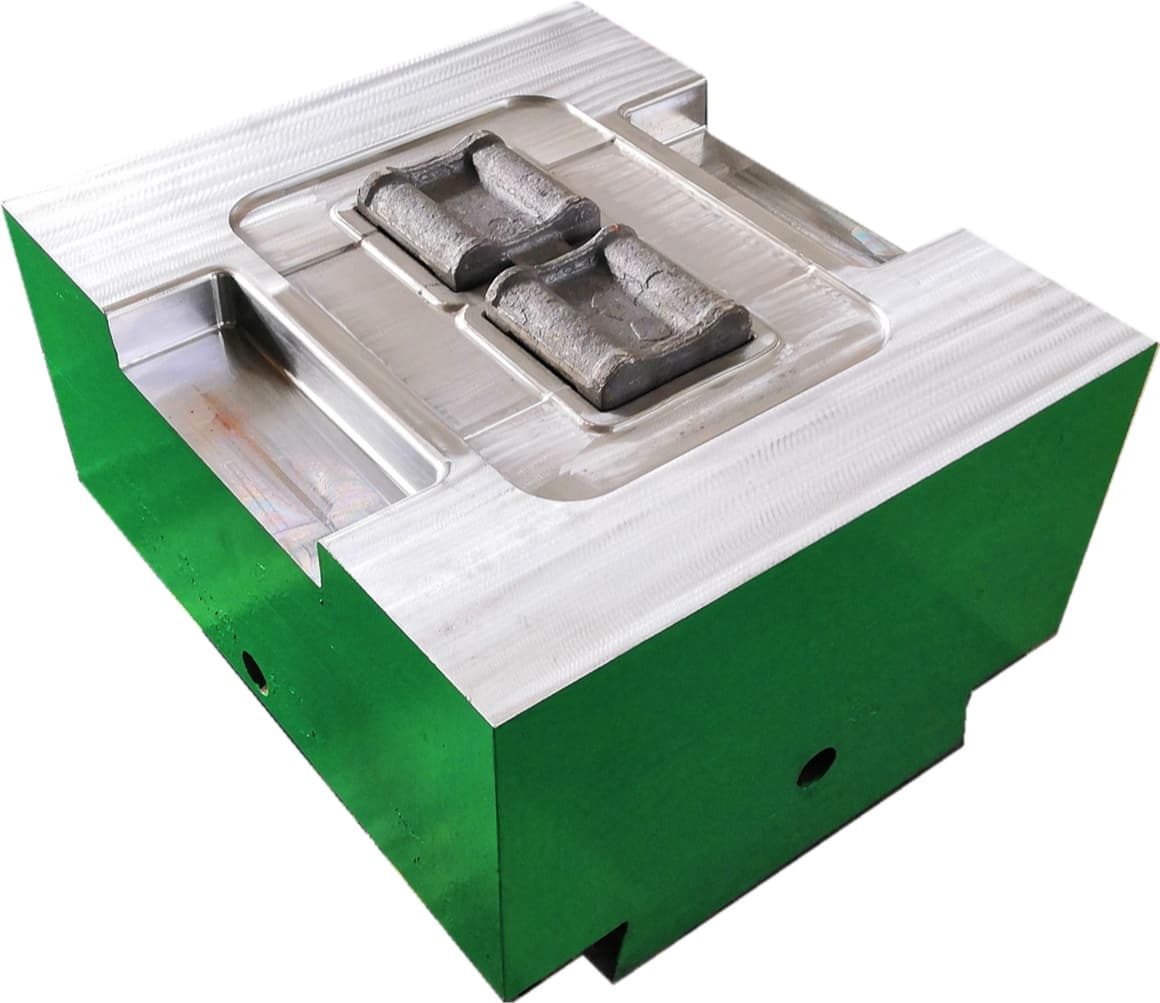
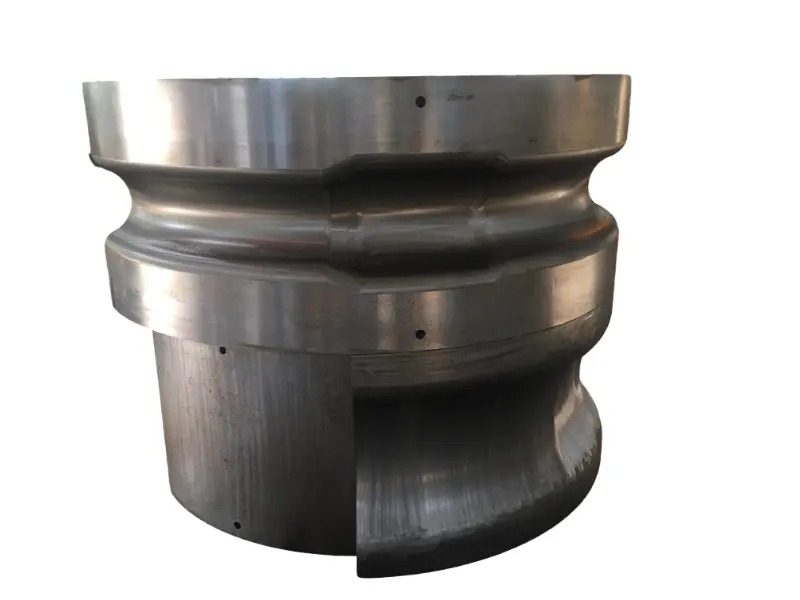
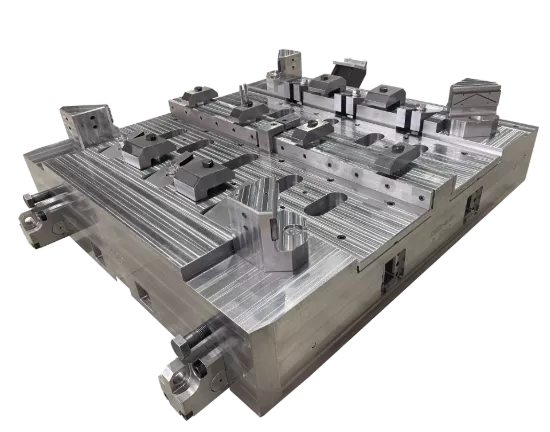
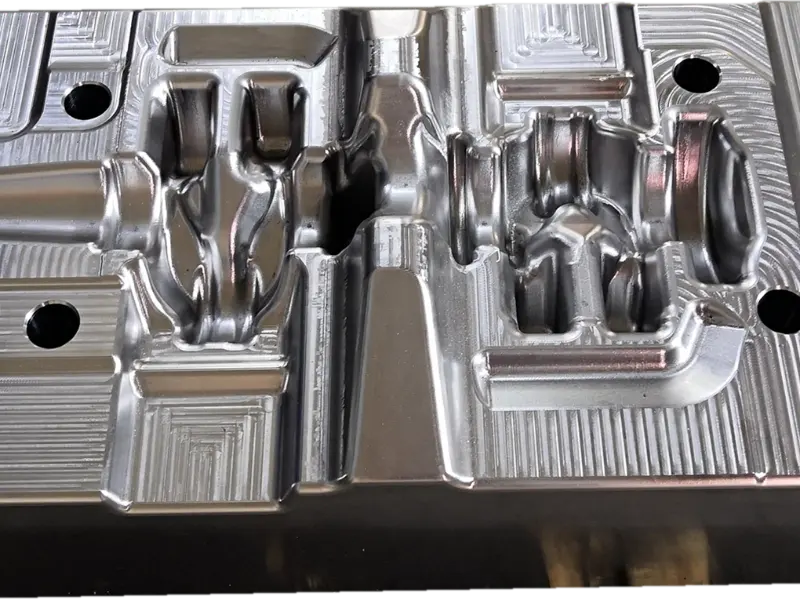
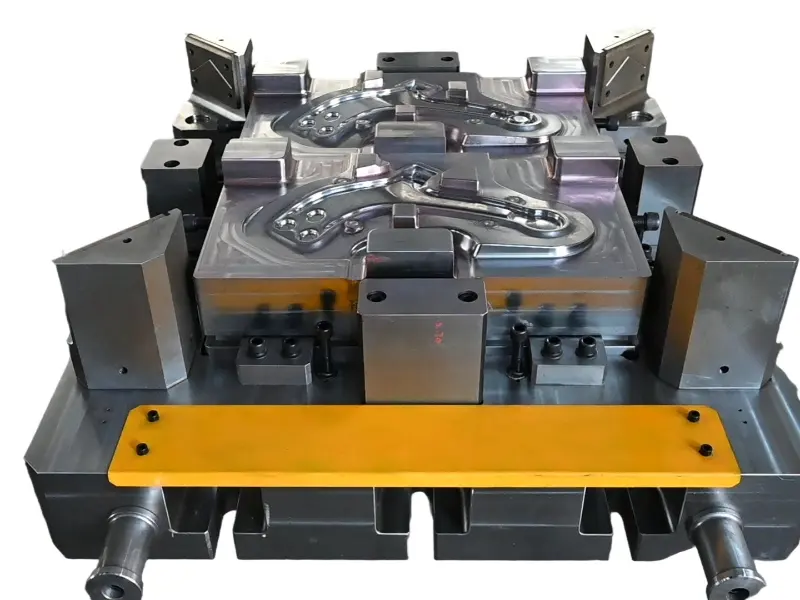
The crankshaft forging die is a core mold specifically designed for crankshaft forging production. Its overall structure adheres to the principles of "mold cavity adaptation and force balance," primarily consisting of core components such as the upper die, lower die, die sleeve, positioning pins, and ejection mechanism.
In terms of material selection, crankshaft forging dies are predominantly made of high-strength hot work tool steel (such as H13, 1.2365, etc.), which exhibits excellent high-temperature strength, wear resistance, thermal fatigue resistance, and toughness.
Additionally, the mold surface undergoes a "nitriding treatment" to further enhance surface hardness and anti-adhesion properties, reducing the adhesion between metal blanks and mold cavities, lowering demolding resistance, and facilitating subsequent mold cleaning and maintenance.
Crankshaft Forging Die
steel:1.2714 / 1.2365 / H13 / 5CrNiMo / 5CrNiMoV / 5CrMnMo / 40CrNiMoA, etc.
Product Description:
Product Usage
The crankshaft, as the “heart component” of power equipment such as engines and compressors, must withstand alternating loads, torque, and impacts during high-speed rotation. It demands extremely high requirements for mechanical properties (e.g., strength, toughness, fatigue life) and dimensional accuracy. The crankshaft forging die is the core tool for achieving “high-quality crankshaft blank forging,” primarily used in the following fields:
Manufacturing of elongated forgings in the automotive industry
This is the most critical application scenario for crankshaft forging molds. Whether it is the gasoline/diesel engines of traditional fuel vehicles or the hybrid system engines of new energy vehicles, their crankshafts require forging processes to form customized cavity structures, producing batches of matching crankshaft blanks. These blanks are then machined, heat-treated, and assembled into core engine components to ensure the stability of power output and service life of automotive engines.
Customized Crankshaft R&D and Small Batch Production
In addition to mass production, crankshaft forging dies can also be used for the research and trial production of new model crankshafts. For new crankshaft design proposals from research institutions and engine manufacturers, small-batch trial production molds can be quickly fabricated to forge prototypes within a short period. This helps R&D teams verify the structural rationality of the crankshaft and the feasibility of forging processes, thereby shortening the new product development cycle and reducing R&D costs.
Manufacturing of Crankshafts for Marine and Engineering Machinery Power Equipment
`The engines of marine vessels (such as diesel engines) and construction machinery (such as excavators, loaders, and cranes) feature larger crankshaft dimensions and greater weight (some marine crankshafts can weigh dozens of tons), while also bearing heavier loads, which imposes higher requirements on the size and strength of forging molds. Crankshaft forging molds can be manufactured through the process of “large-scale mold blank forging + CNC gantry milling precision machining” to produce oversized molds (with single sets weighing several tons), meeting the integral forging demands for large crankshafts. This approach avoids the issue of insufficient joint strength caused by segmented crankshaft forging, ensuring the power reliability of marine vessels and construction machinery under harsh working conditions.“
Generator / Compressor Crankshaft Manufacturing
For industrial equipment such as diesel generator sets and air compressors, the crankshaft must operate continuously at high speeds for extended periods, demanding stringent requirements for fatigue strength and wear resistance. By optimizing the fillet transitions and draft angles of the crankshaft forging mold, stress concentration points in the crankshaft blank during forging can be reduced. Combined with isothermal forging technology, the metal microstructure of the crankshaft blank is improved, ensuring stable long-term operation after subsequent quenching and tempering. These crankshafts are widely used in scenarios like factory backup power supplies and mine compressed air systems.