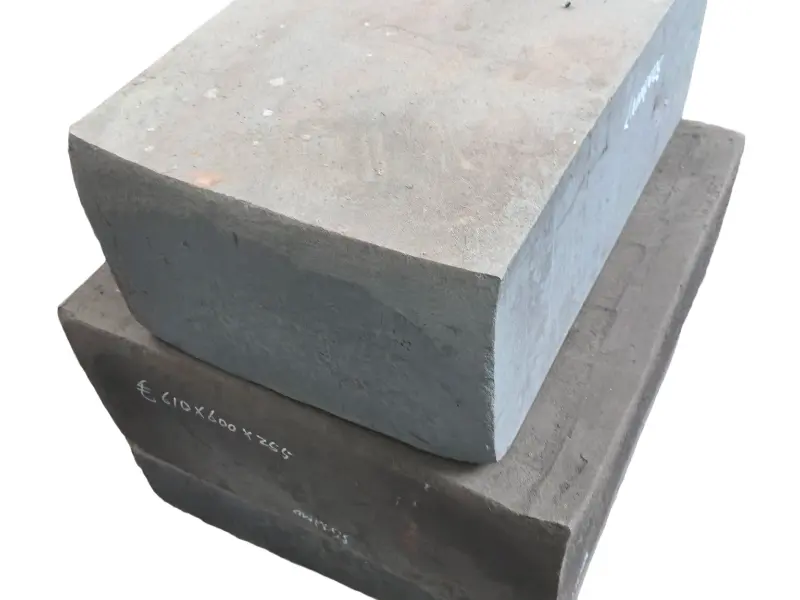
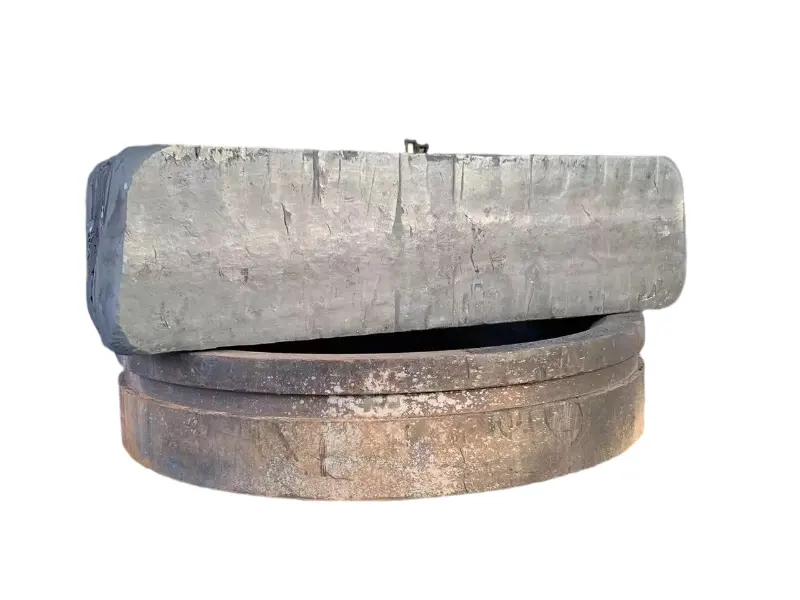
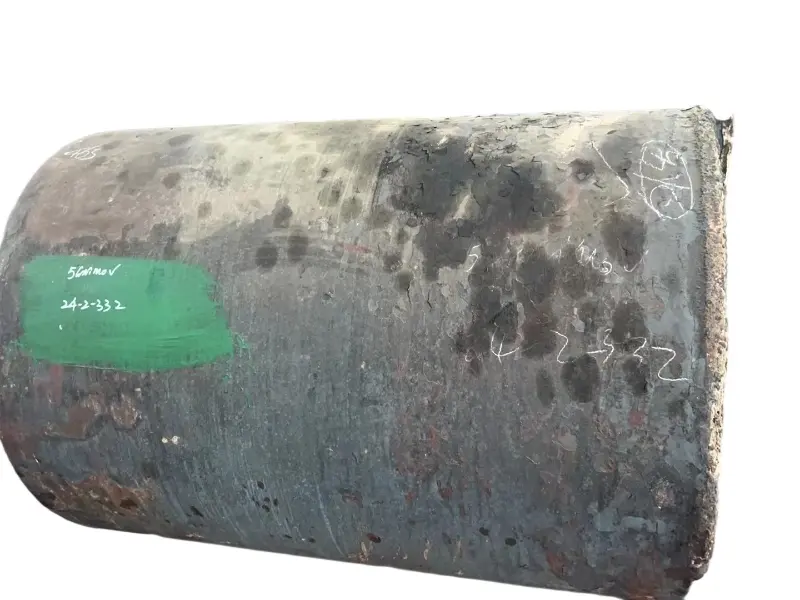
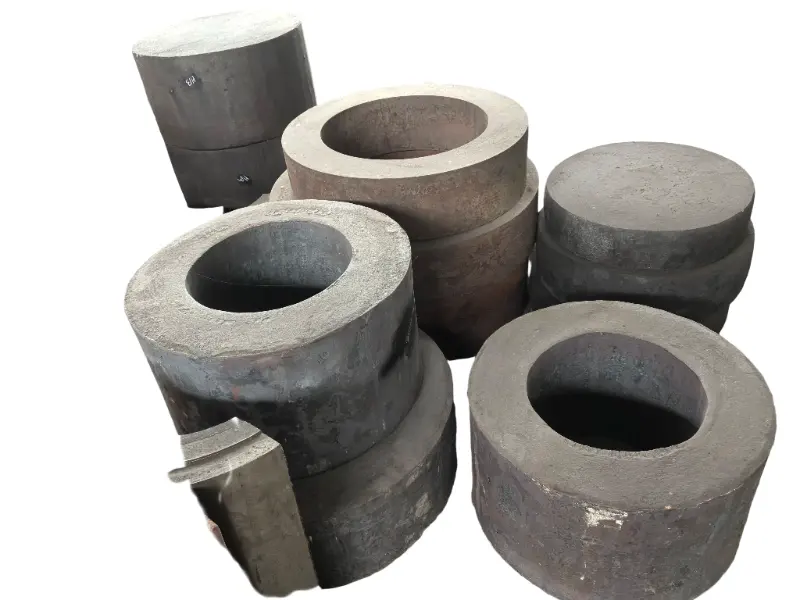
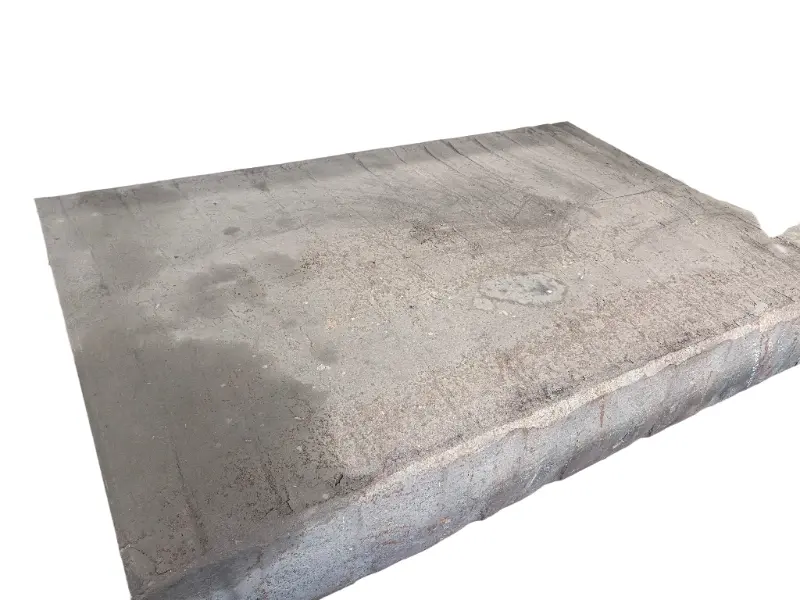
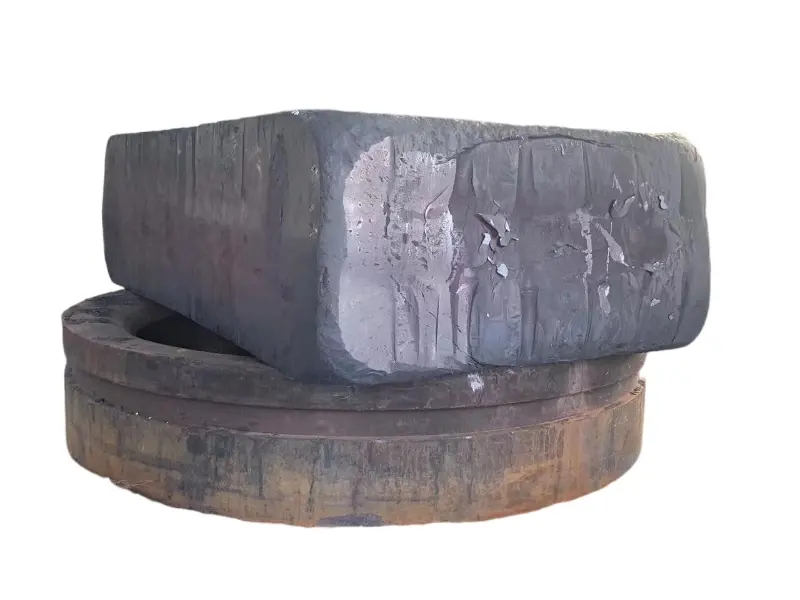
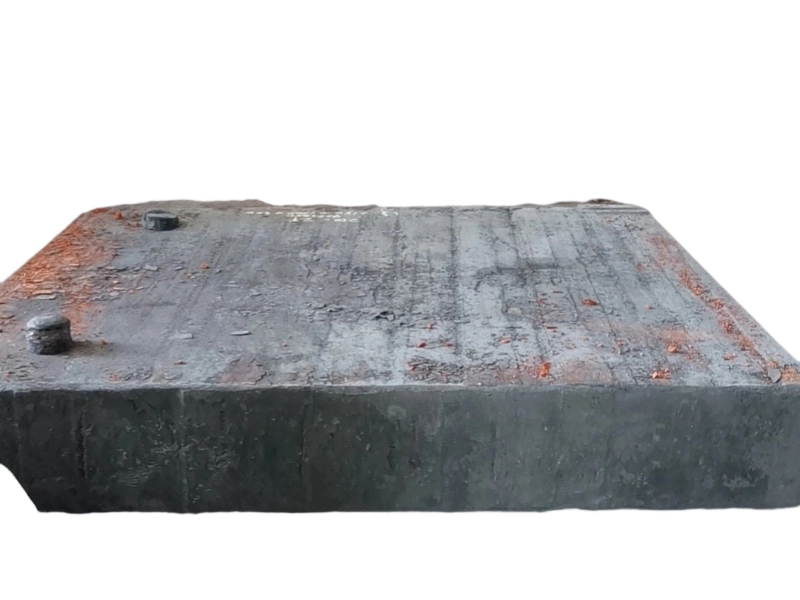
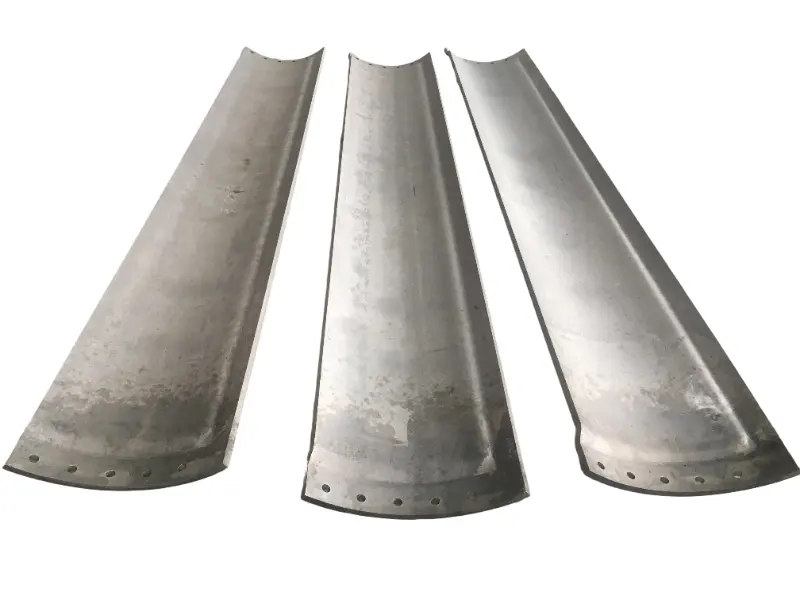
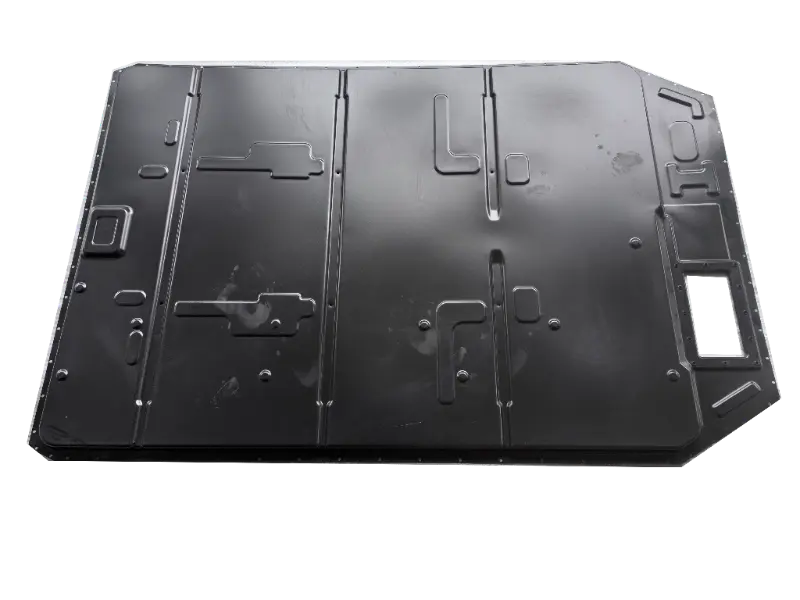
Forging is the process of applying external force to a metal billet, causing it to undergo plastic deformation under the action of a mold or forging hammer, thereby obtaining a metal product with specific shape, size, and mechanical properties. Forged parts are metal components with specific shapes, sizes, and mechanical properties made from metal materials (such as steel, aluminum, copper, titanium alloys, etc.) through forging processes (applying external forces to cause plastic deformation of the metal billet). The core advantages are "dense organization, excellent mechanical properties, and strong structural stability". They are key raw materials for core load-bearing and transmission components in mechanical manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, energy and other fields. Compared with castings and welded parts, forged parts have irreplaceable strength, toughness, fatigue life and other aspects.
Forged Parts
steel:1.2714 / 1.2365 / H13 / 5CrNiMo / 5CrNiMoV / 5CrMnMo / 40CrNiMoA /42CrMo, etc.
Product Description:
Product Usage
High quality steel materials (such as carbon structural steel, alloy structural steel, stainless steel, etc.), copper alloys, aluminum alloys, and other metal materials are selected for forgings. Multiple forging processes such as free forging, die forging, and membrane forging can be used according to customer needs. In terms of performance, after forging, the grains inside the metal are refined and the structure is denser, effectively eliminating defects such as porosity, looseness, and inclusions that occur during the casting process of the metal billet. Therefore, it has high strength, high toughness, good wear resistance, and fatigue resistance. The forging materials include structural steel forgings, alloy structural steel forgings, stainless steel forgings, high-temperature alloy forgings, and non-ferrous metal forgings.