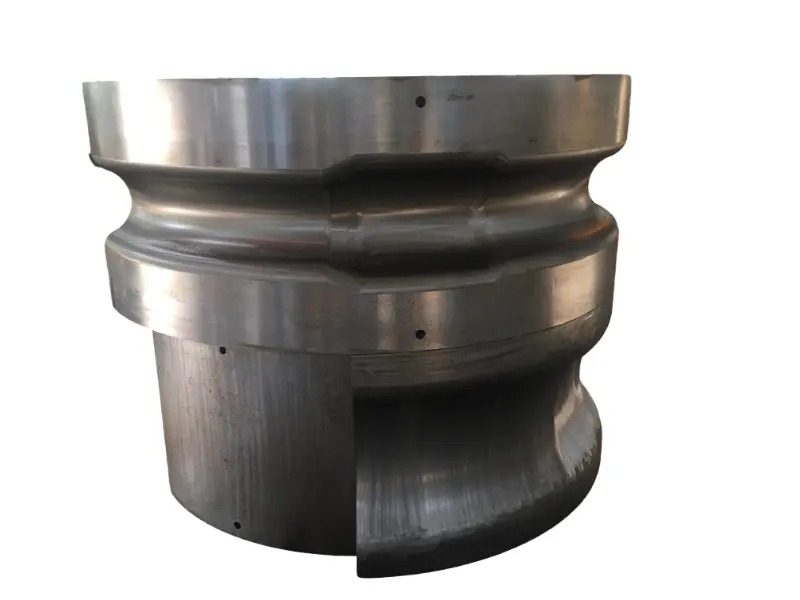
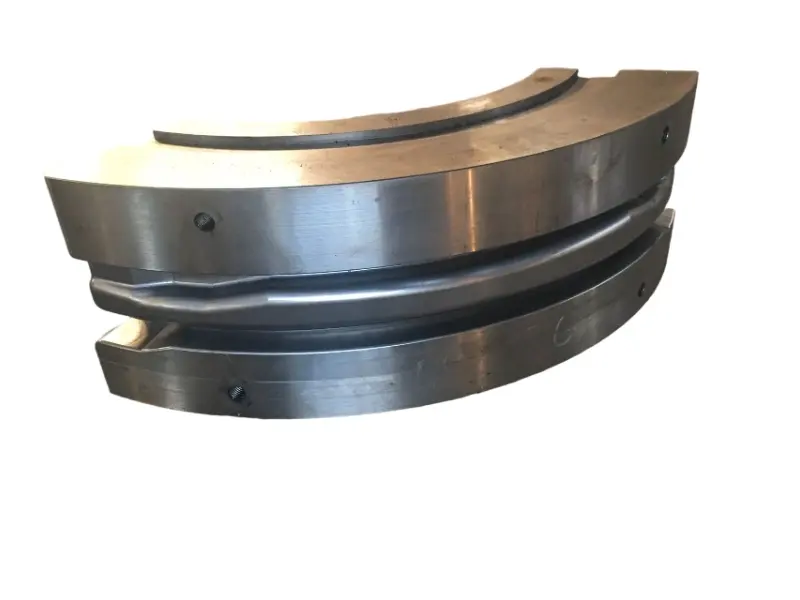
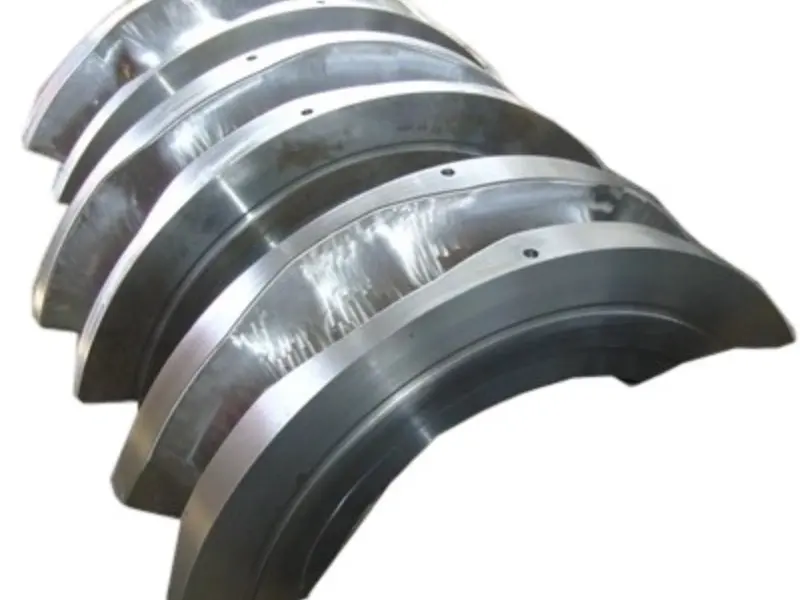
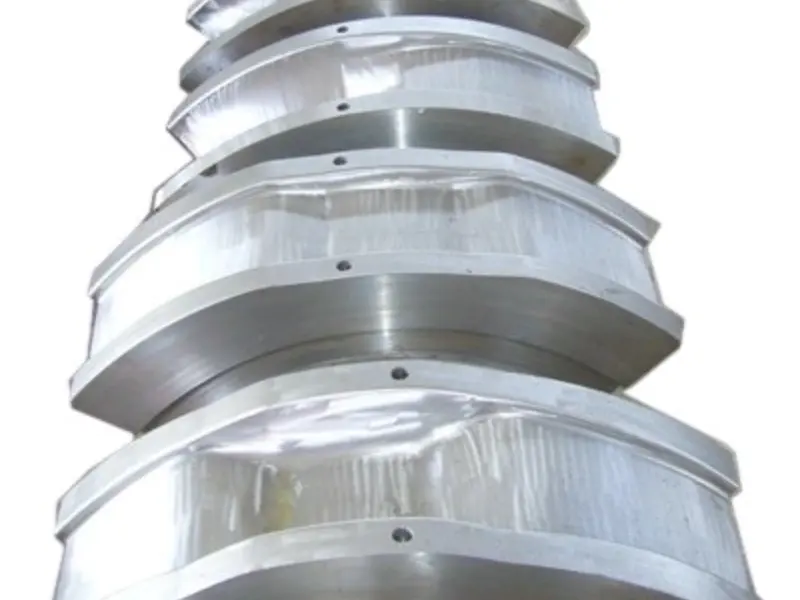
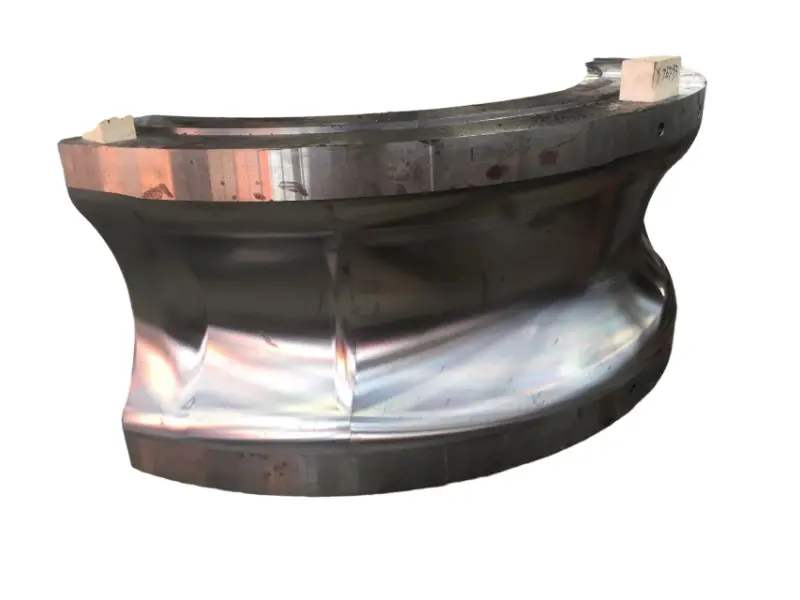
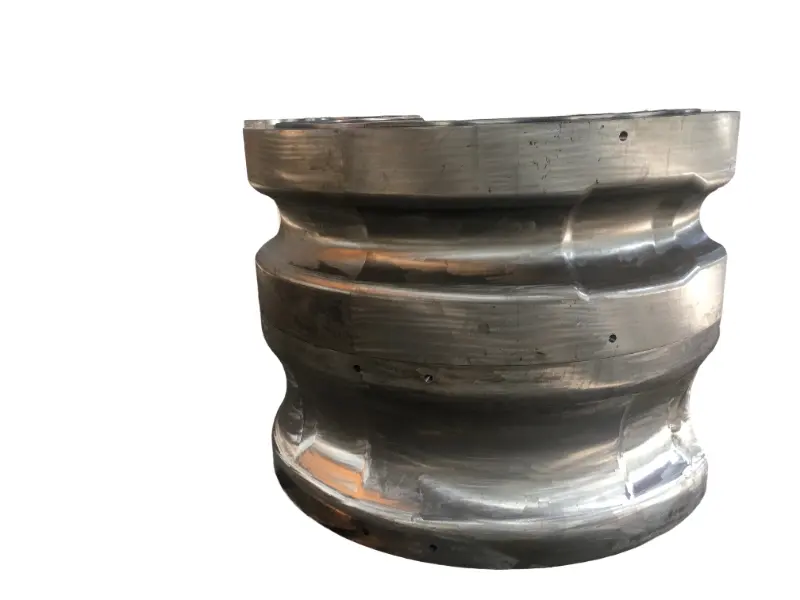
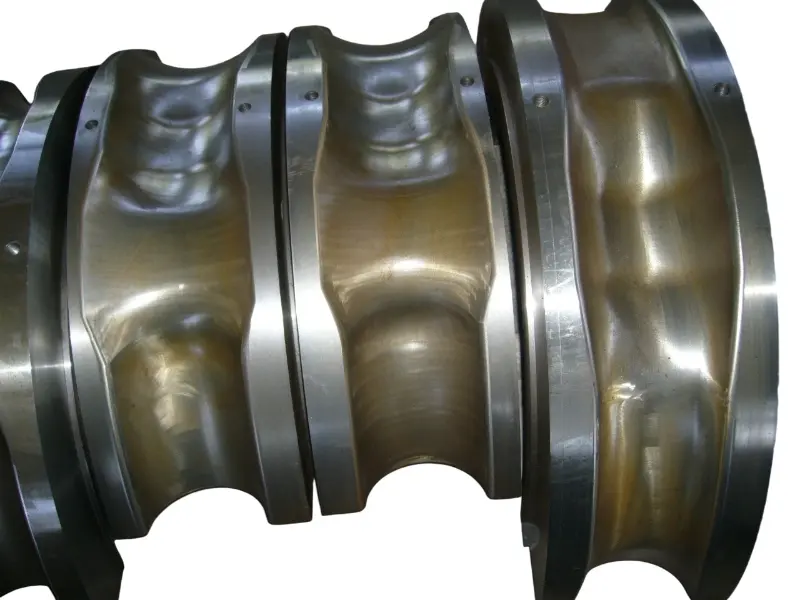
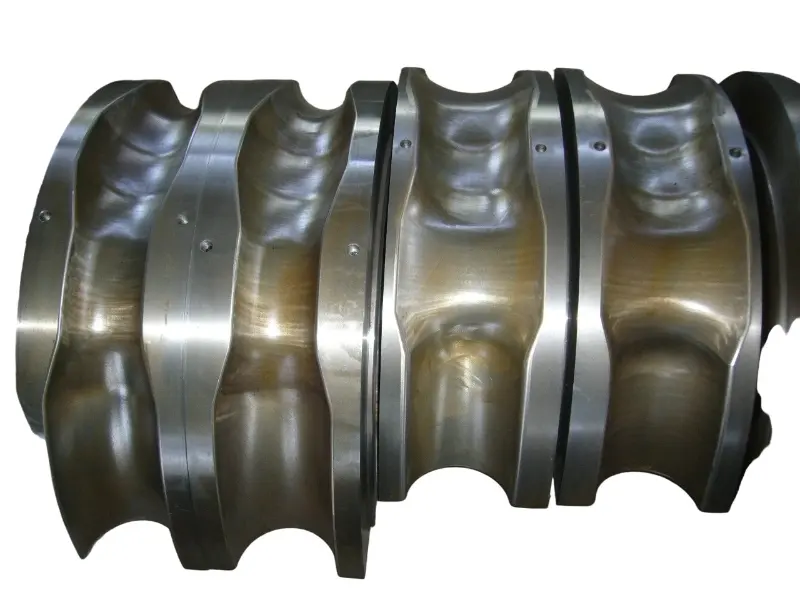
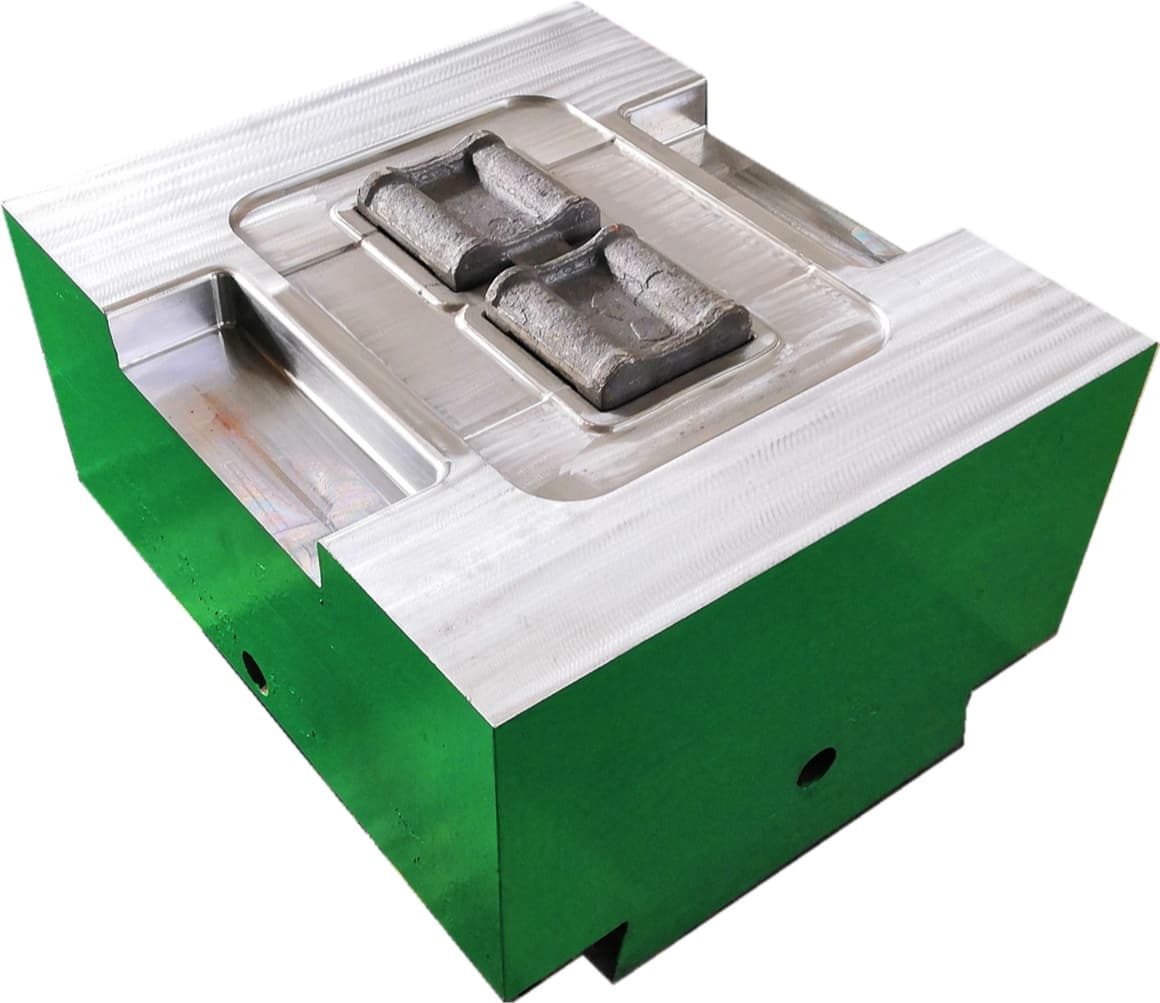
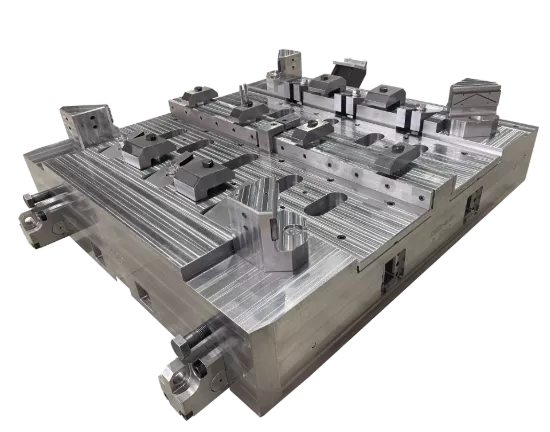
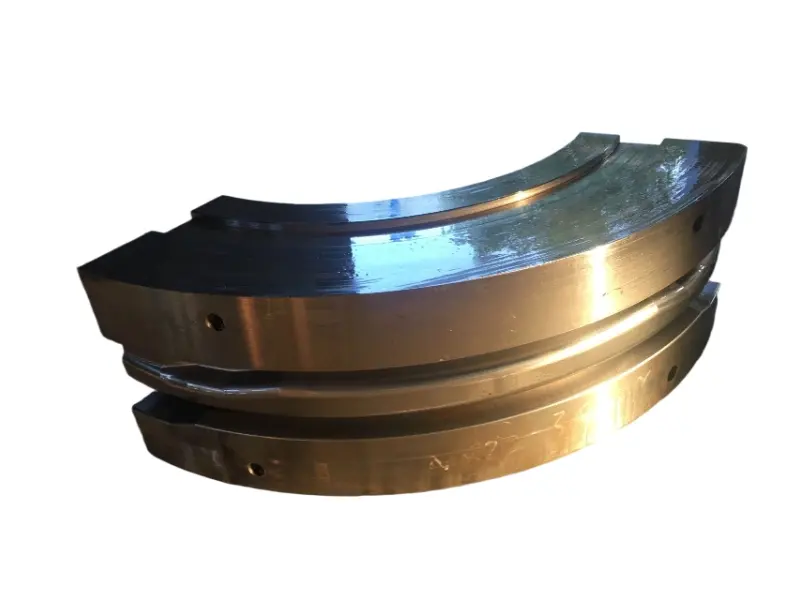
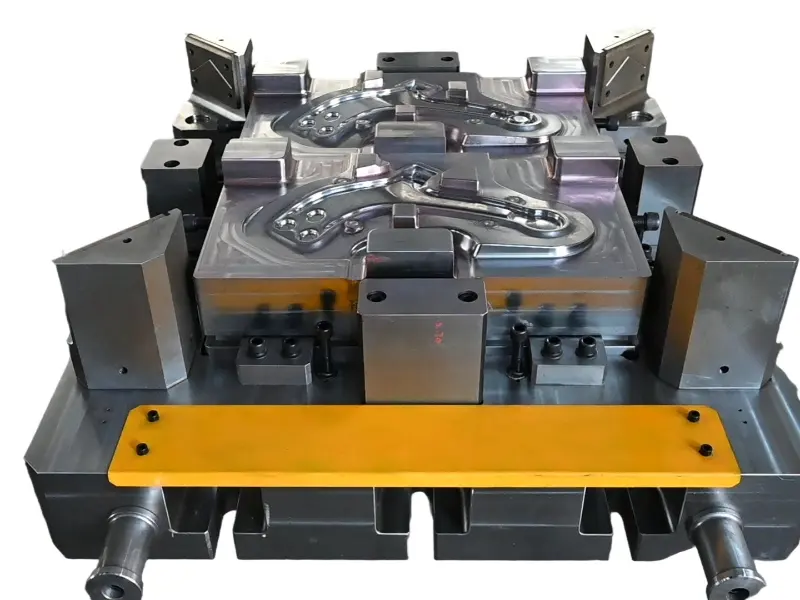
Rolling forging die is a professional fixture designed specifically for roll forging machines, which achieves progressive forming of metal billets through the rolling action of one or more pairs of rotating dies. Its core advantages lie in "continuous forming, high efficiency, high material utilization rate, and suitability for mass production of long strip/symmetrical parts". It is a key equipment for the manufacturing of long strip forgings (such as automotive connecting rods and agricultural plows) in the fields of automobiles, agricultural machinery, engineering machinery, etc. It is also a way of making complex forging products.
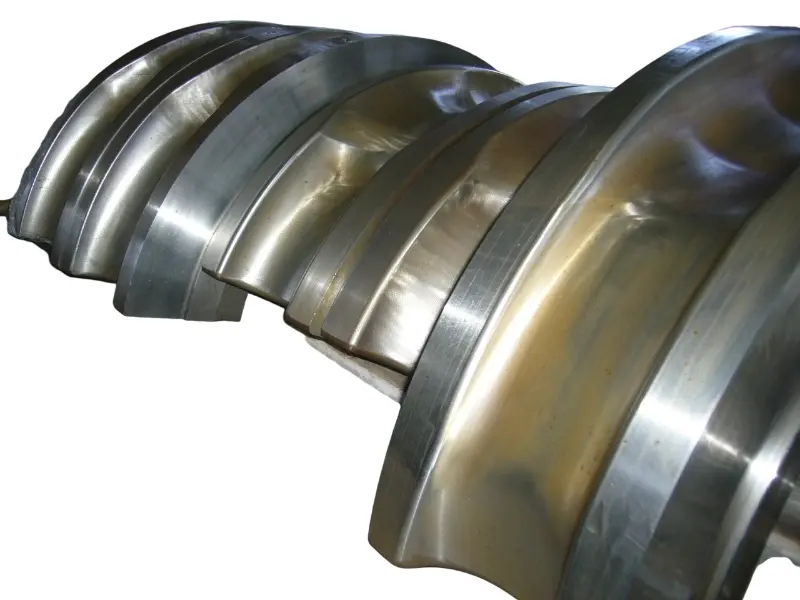
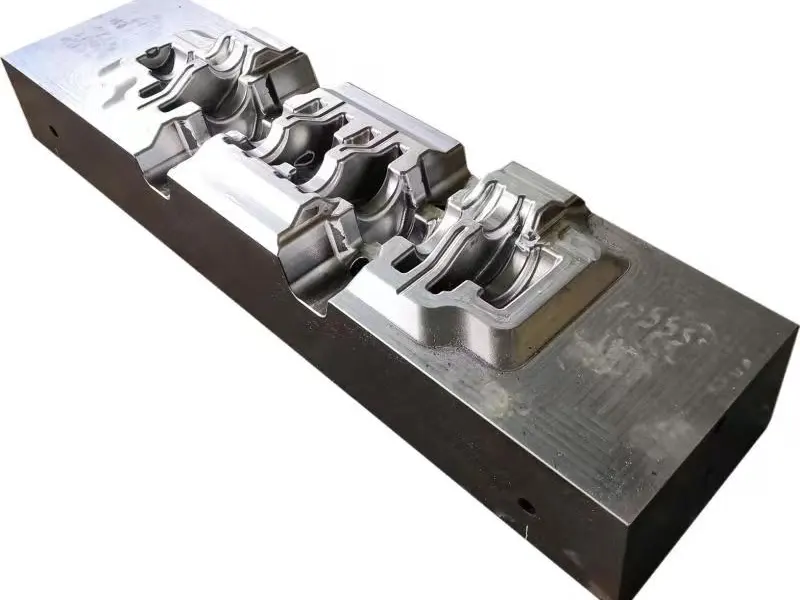
From a structural perspective, the roll forging die adopts a "paired symmetrical design", usually consisting of an upper roll die and a lower roll die. In some complex forming scenarios, multiple sets of continuous roll dies (such as pre roll dies and final roll dies) may be set up. The circumferential surface of each pair of roller molds is machined with a cavity that matches the shape of the forging. The cavity is designed according to the principle of "progressive forming", and the shape of the cavity gradually approaches the final shape of the forging from the inlet end to the outlet end of the billet, ensuring that the metal billet flows smoothly along the axial direction during the rolling process and avoiding local accumulation or tearing.
In terms of material selection, due to the need to withstand friction and wear during continuous rolling, high temperatures (850-1150 ℃), and periodic loads, high-strength hot work die steels (such as H13 steel and 5CrNiMo steel) are often used for roll forging molds.
In terms of process adaptability, roll forging molds are compatible with two mainstream processes: hot roll forging and warm roll forging. Hot roll forging is suitable for difficult to deform materials such as medium and high carbon steel and alloy steel, while warm roll forging is suitable for low carbon steel and non-ferrous metals that require high surface quality.
Rolling Forging Die
steel:1.2714 / 1.2365 / H13 / 5CrNiMo / 5CrNiMoV / 5CrMnMo / 40CrNiMoA, ect.
Product Description:
Product Usage
Rolling forging dies are widely used in fields that require high batch, efficiency, and cost control of forgings due to their characteristics of “continuous and efficient, suitable for long strip forgings”. The specific uses are as follows:
Manufacturing of rail transit and general machinery forgings
In the field of rail transit, roll forging molds are used to produce components such as hook and tail frames and middle pull rods for railway trains. Through the progressive forming of roll forging molds, the components are made into blanks and then forged into shapes using other molds. In the field of general machinery, roll forging molds are used to produce long strip parts such as machine tool spindles, chain plates for conveying machinery, and roller shafts for textile machinery. Roll forging molds can achieve batch and efficient forming of these parts, while improving the mechanical properties of the parts, reducing the manufacturing cost of general machinery, and adapting to the production needs of different industries such as machine tools, textiles, and logistics.
Manufacturing of elongated forgings in the automotive industry
This is the core application scenario of roll forging molds, mainly used for producing long strip forgings for automotive transmission systems, chassis systems, and engine systems. For example, the connecting rod of an automobile engine can be gradually formed into a “rod body big head small head” through continuous rolling of multiple sets of rolling forging molds, meeting the large-scale production needs of the automotive industry; The control arm and pull rod of the car chassis are formed by roll forging molds, which can distribute the metal fibers inside the forging along the direction of force, significantly improving the fatigue resistance and ensuring the structural stability of the car during driving; At the same time, the roll forging die can be used in conjunction with other forging dies to make blanks for the product, which is then forged into the final product through a closed forging die.
Manufacturing of key forgings for agricultural machinery
In the field of agricultural machinery, roll forging molds are used to produce elongated working parts of agricultural machinery, such as plows, rake teeth, harvester blades, etc. As the core component of cultivated land, plowshare needs to have high strength and wear resistance. Through continuous rolling of roll forging molds, it meets the wear resistance requirements of deep plowing operations;
Manufacturing of engineering and mining machinery forgings
In the field of construction machinery, roll forging molds are used to produce rectangular forgings such as bucket rods, boom connecting pins, and track plates for excavators and loaders.